Admin
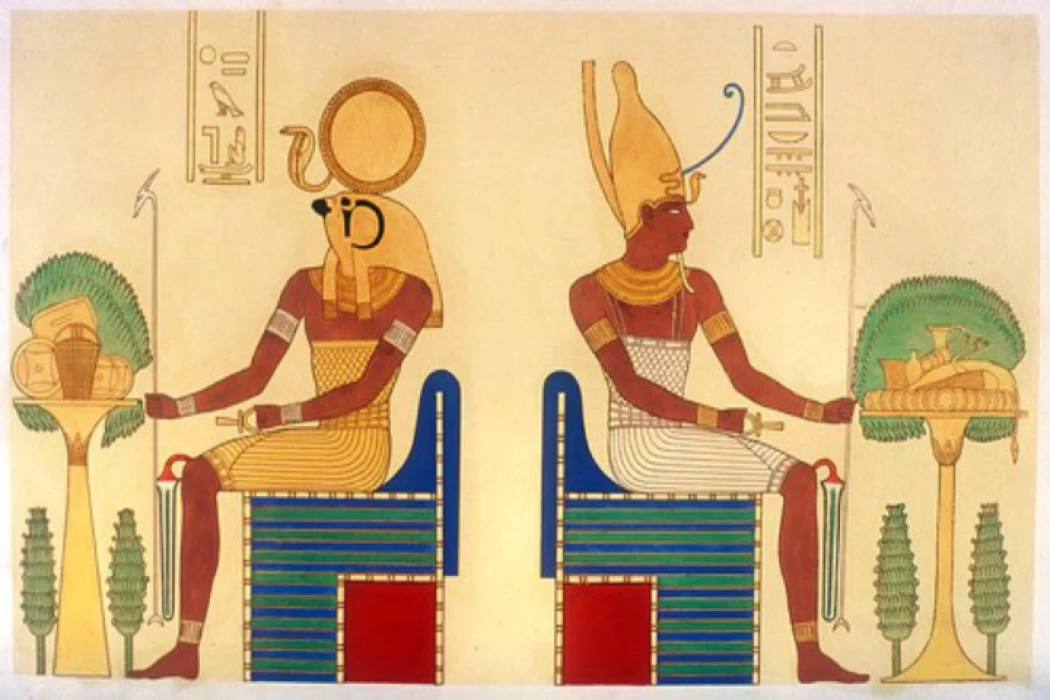
Amun Ra is one of the major gods in Egyptian mythology, In hieroglyphics, Amun, is the god of the sun, wind, and fertility. His name means the hidden. The worship of Amun (and later Amun-Ra) and the religion associated with them is one of the most complex theologies of ancient Egypt. Discover the temples of ancient Egypt with the great inscriptions about Amu Ra with Cairo Top Tours professional team.
Admin
Isis the Egyptian Goddess
Isis is one of the most beloved goddesses of the ancient Egyptians, along with her husband Osiris and her son Horus. The first place for the spread of worshipping the goddess Isis: is the Mediterranean after the establishment of Greek rule in Egypt during the fourth century BC. Book your tour to watch the temples of the great goddess Isis with Cairo Top Tours professional team.
Admin
Osiris the Egyptian god of the afterlife and resurrection
Osiris is the god of resurrection and judgment and the head of the court of the dead among the ancient Egyptians. he is the only god who competed with the worship of the god Ra; In addition, He is one of the main sacred ennead gods in the ancient Egyptian religion. According to the ancient Egyptian religious myths, Osiris was the brother of Isis, Nephthys, and Seth, and he married Isis. Book your tour with Cairo Top Tours’ Egyptologists to learn about Osiris.
Admin
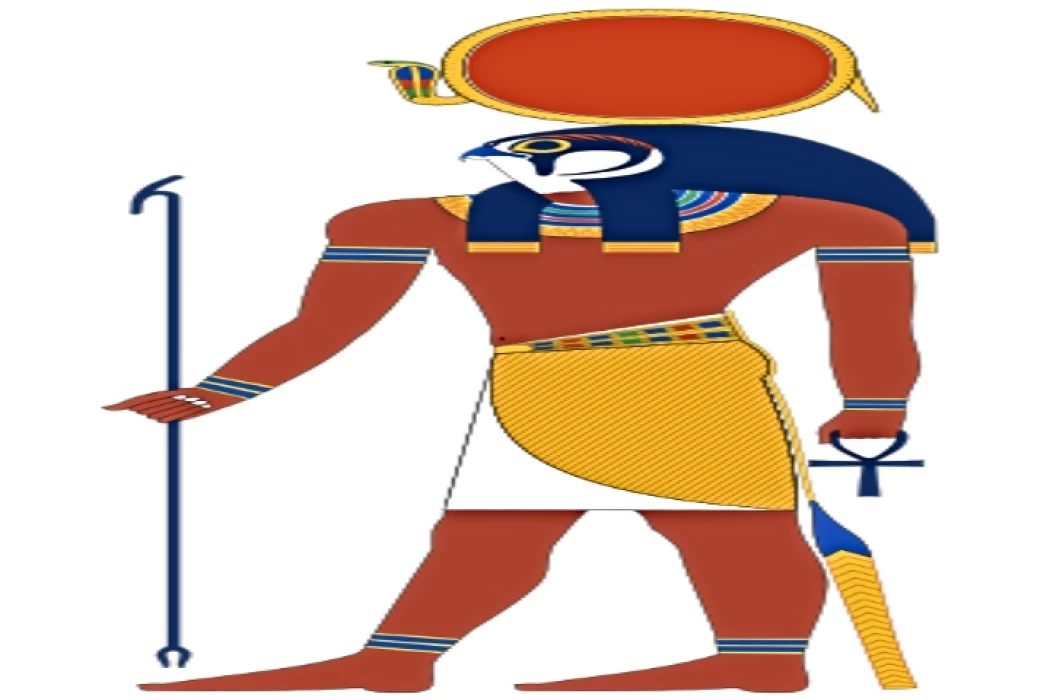
Horus | The God with the falcon head
the god Horus is considered one of the most important and oldest Egyptian gods in ancient Egypt. He is the god of goodness and heaven, and many temples were constructed specially for him. Horus is the first Egyptian deity to have the form or the symbol of a falcon. Come to Egypt and book your tour with the professionals of Cairo Top Tours to see Horus temple.
Admin
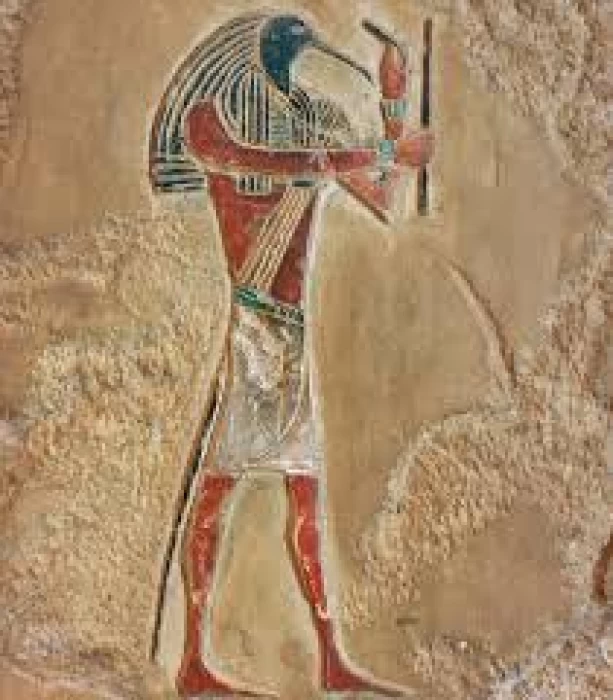
God Thoth | Wisdom’s god in ancient Egypt
The god Thoth or Thoth or Tut was the god of science, knowledge, and wisdom for the ancient Egyptians and was one of the most prominent eight gods in the city of Ashmunayn. His symbol was the head of an ibis bird. visit Egypt, and be accompanied by certified Egyptologists to learn more about the Egyptian gods.
Admin
Goddess Nephthys | Symbol of birth and death
The god Nephthys symbolizes birth, death, concealment, and darkness for the pharaohs and ancient Egyptians. She is a member of the Heliopolis Ennead. Discover the myths, temples, and tales about her while visiting Egypt with Cairo Top Tours.
Admin
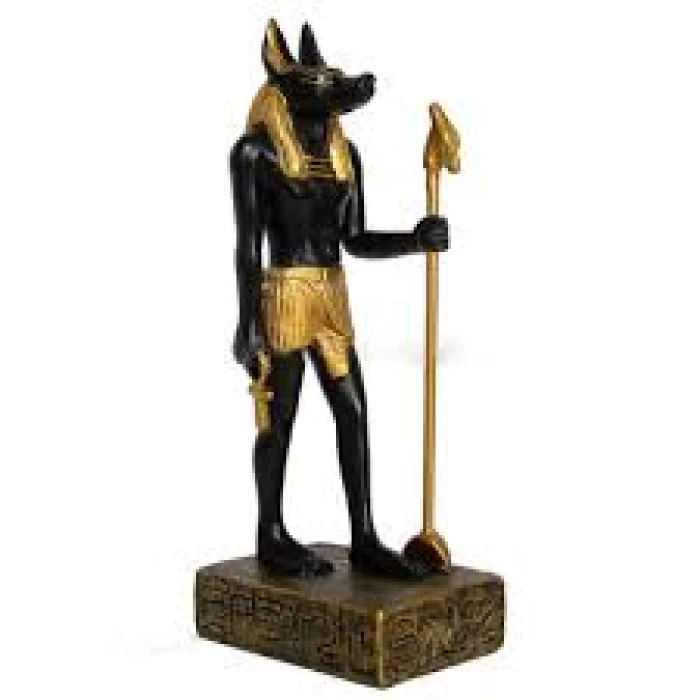
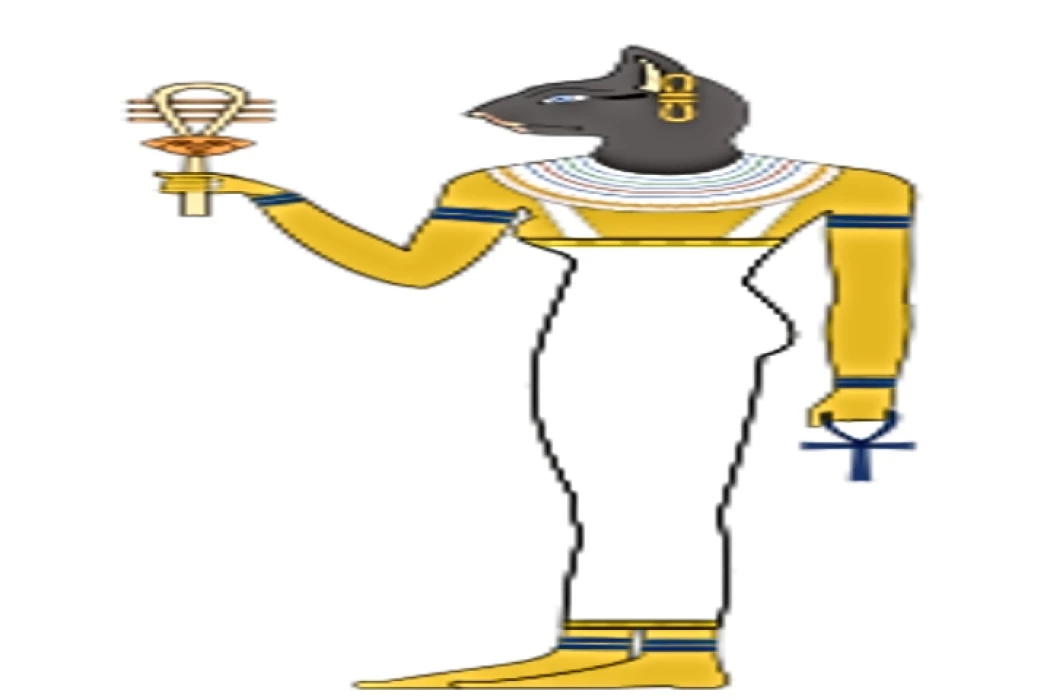
Anubis: Guardian of the Underworld and Protector of the Mummified Dead in Ancient Egypt
Anubis, the ancient Egyptian god of the underworld, later associated with mummification and funerary rites, symbolized protection for the dead. Known as "Imy-ut" and "Lord of the Sacred Land," Anubis ensured proper mummification and guided souls in the afterlife
Admin
Learn all about the Book of the Dead
Discover the mystical world of ancient Egypt's Book of the Dead, where spells and rituals guided souls through the afterlife. From lavish tombs to powerful artifacts, explore the journey to immortality and the beliefs that shaped Egyptian civilization. Perfect for Egypt travel guides, day tours, and shore excursions, this journey into Egypt’s past unveils secrets preserved on papyrus, walls, and mummies, inviting travelers to experience the magic of Egyptian history.
Admin
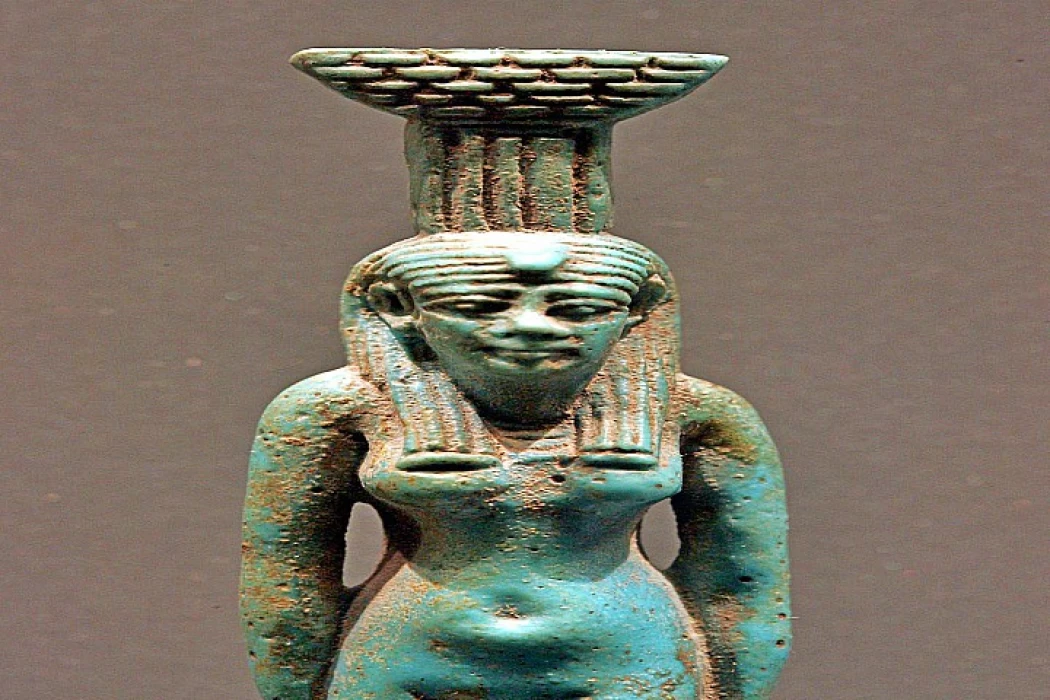
A Symbol of Power and Protection in Ancient Civilizations
Mut is one of the oldest goddesses embodying the sky and therefore had great importance in the beliefs of ancient Egypt. The cult of Mut increased in importance during the New Kingdom and Amenhotep III had a sacred lake built in the Temple of Karnak for her worship.
Admin
Diversity of Deities in Ancient Egyptian Culture
Ancient Egypt's rich tapestry of gods reflects its complex culture, with over 1,500 deities representing natural forces, social structures, and abstract concepts
Admin
Osiris's Myth | The Tale of Isis and Osiris
The myth of sacrificial love that made Isis and Osiris the most beloved gods of the ancient Egyptians and made the god Six despised for doing evil and attempting to kill his brother is the story of Isis and Osiris, the pharaonic love myth that dates back more than a thousand years before the stories of Qais and Lily or Romeo and Juliet.
Admin
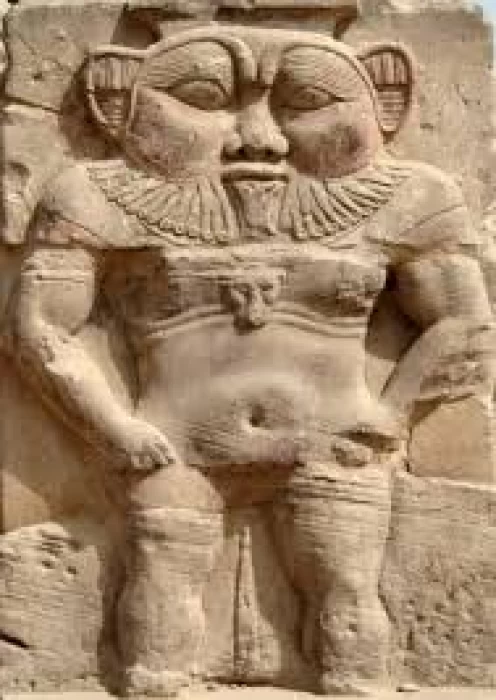
God Bes | God of Childbirth | Ancient Egyptian Dwarf God
One of the gods of ancient Egypt, Bess enjoyed great popularity under the New Empire. His representation is a fan-shaped chin on a puffy-cheeked dwarf that is meant to terrorize the unsullied. He was revered in the Roman era as the Healer, who was armed with a shield and sword, and was frequently mentioned in the Temple of Dandara.
Admin
God Sobek
The god of nature in ancient Egypt was known as Subic, or Sobek. He was linked to military might, fertility, and royal authority. Along with his evil-repelling properties, he was also revered as a deity of protection against perils, particularly those brought on by the Nile's frequent floods.
Admin
God Atum
Atum is an ancient Egyptian deity representing creation and the setting sun. As one of the primordial gods, he is often depicted as a self-created entity who emerged from the primordial waters of chaos to form the world, embodying both the sun and the creative force of the universe.
Admin
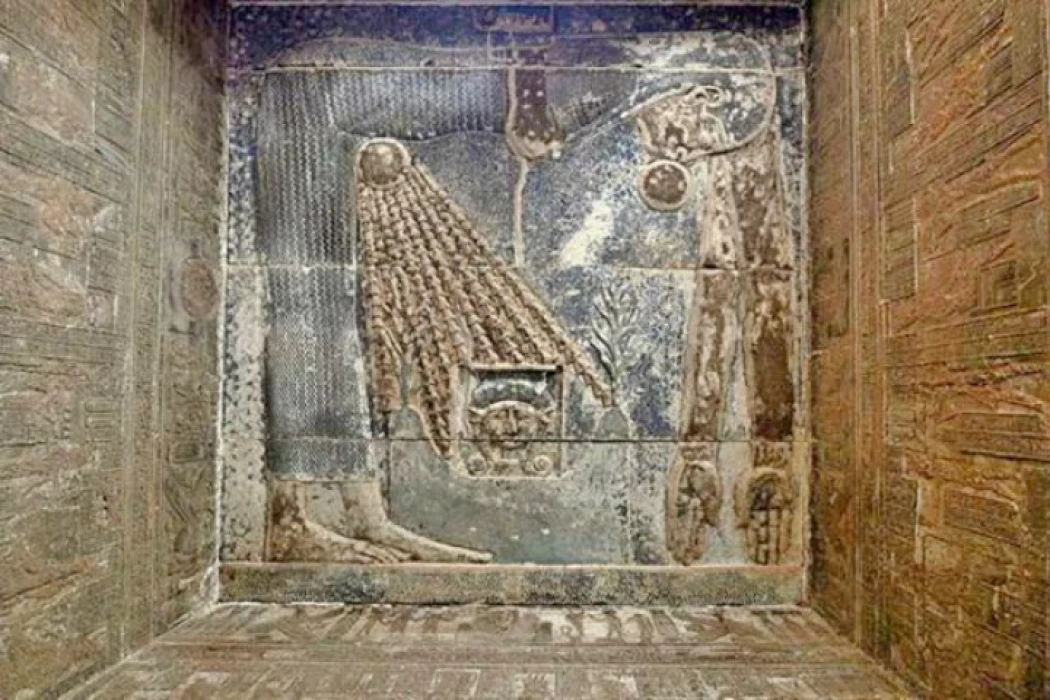
God Aton | Aten God of Egypt
As the sun god, Aton was revealed by King Akhenaton and is revered by all races. He is represented by a solar disk with rays that end in human hands, giving the royal family life and prosperity both during and after Akhenaton's death. Among the gods of Egypt, Amun made a comeback, regaining his position at the top.
Admin
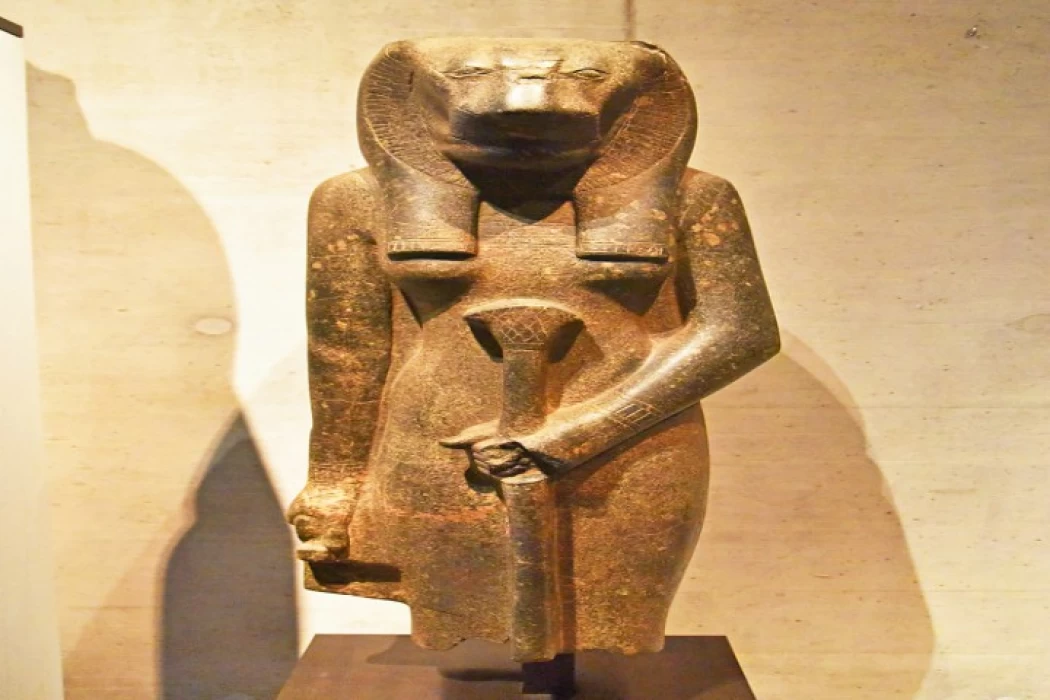
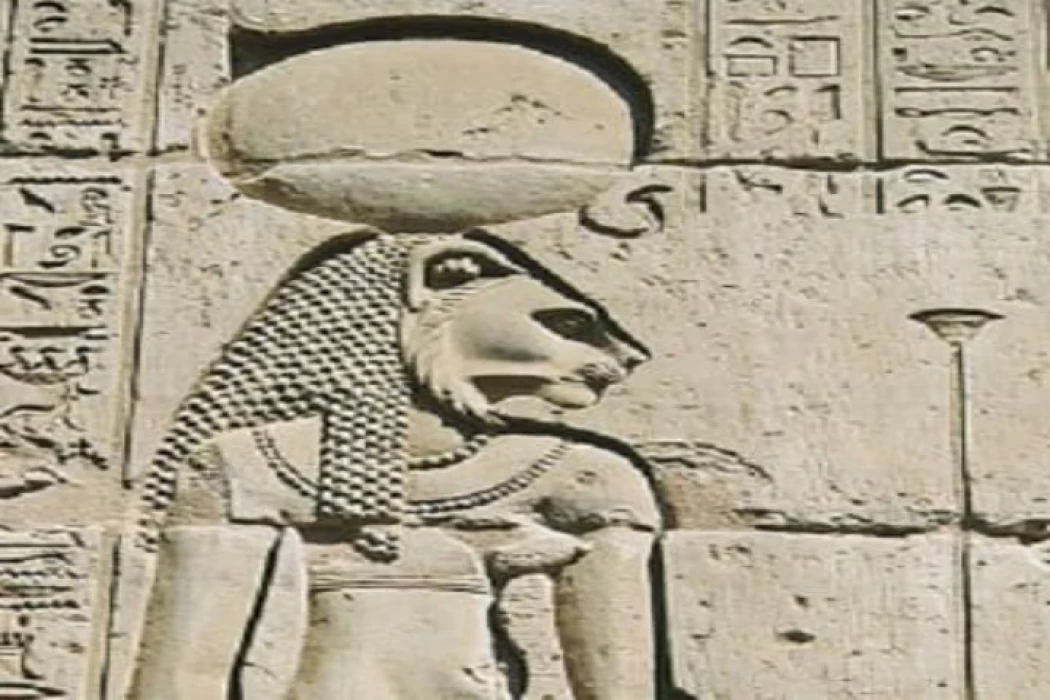
Goddess Sekhmet
Sekhmet is a mythological figure of ancient Egypt, depicted as a lioness-headed woman seated on a throne. Among her titles are the great lady, the beloved of Ptah, the eye of Ra, the lady of war, the lady of the earthly, "Upper and Lower Egypt", the mighty, and many other titles, meaning that her name is the most powerful, and she was worshipped at the entrances of the valleys, especially in Upper Egypt.
Admin
Goddess Nut | Goddess of the Sky
In ancient Egyptian religion, Nut is the goddess of the sky, and she is typically shown with stars. She is the sister of Jeb, the earthly god; her father is Shu, the god of the air; and her mother is Tefnut, the goddess of moisture (or, as other historians have it, the goddess of fire). These are the religious beliefs of the ancient Egyptians.
Admin
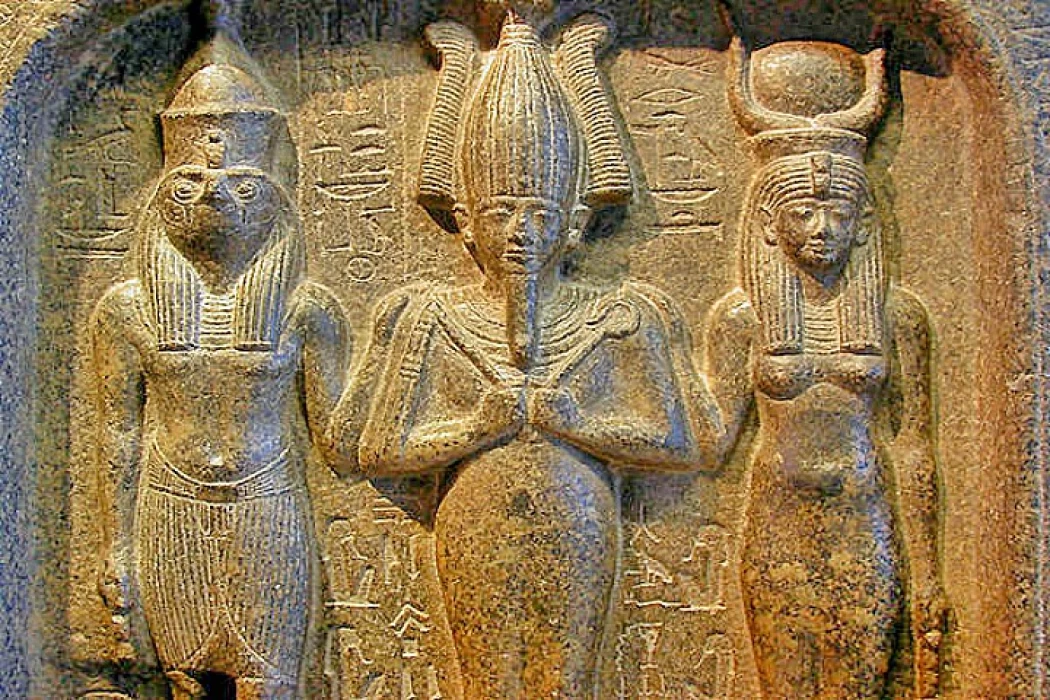
Goddess Mut | Egyptian Goddess of Heaven
Her name means "Death" and "Mother" and she is Amun's wife. In ancient Egypt, she was the mother of the gods. Over thousands of years, her name and pronunciation have evolved in numerous cultures and civilizations. Often shown as a queen, she is incanted as a lioness and has a white crown, often called a double crown, and a headpiece stripped by vultures.
Admin
God Khonsu | God of the Moon
In Egyptian mythology, Khonsu, also called the deity of the moon, is linked to medicine. He was also revered as the guardian of the sick, a deterrent to bad spirits, and a symbol of birth and earthly fertility. He was regarded as the son of "Amun and Mut" from ancient times, and his Karnak temple is extraordinarily well-preserved.
Admin
God Geb | God of the Earth
Geb is a god of the ancient Egyptians and a member of the "Tarsus Heliopolis" mythology. He is the brother of the sky goddess Nut, according to ancient Egyptian religious legend, and they are the two sons of Shu, the deity of air, and Tefnut, his wife, who was once thought to be the goddess of moisture and water but is now identified as the goddess of "fire" by archaeologists.
Admin
God Khnum | God of the Waters
In the religion of ancient Egypt, Khnum was a god who was portrayed as a ram or as a man with two horns and a ram's head. In the belief of the ancient Egyptians, Khnum used a potter's wheel to physically create humanity from the muck of the Nile. The god who brought the Nile to create life on its banks, he was revered in Aswan, Memphis, and Esna, among other places in Egypt.
Admin
God Shu | Egyptian God of Air
Not only did Shu symbolize light, but he was also regarded as a calm and good god, much like the fresh air that arrived in Egypt. Shu was one of the most significant gods among the Egyptian pantheon. He was the god of the air, and his name meant emptiness since it was the space that separated the sky from the earth.
Admin
Goddess Tefnut | Goddess of Humidity and Rain
One of the gods of ancient Egypt, Tefnut is a member of the holy Tasus of Heliopolis. In addition to creating the world, this ninth also discovered the worlds of water, earth, and sky, according to Egyptian mythology. Tefnut was also referred to as "the truth" and "the Nubian cat" at times. Originally thought to symbolize dampness, archaeologists chose to characterize it as a fire emblem.
Admin
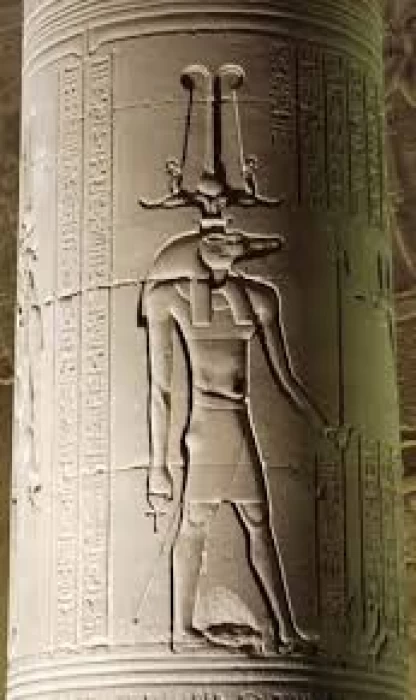
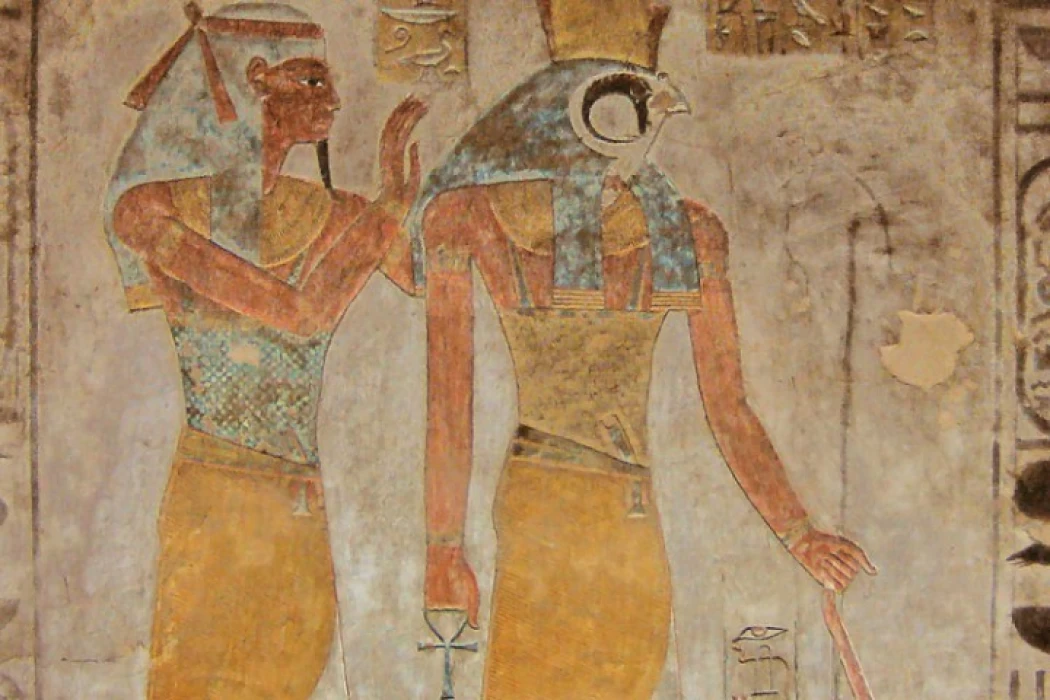
The story of the god Re-Hor-Achti
Re-Hor-Achti, a significant deity in ancient Egyptian mythology, symbolizes the sun and horizon. A syncretic figure, he combines elements of Ra and Horus, symbolizing light and power. Often depicted as a falcon-headed figure, he traverses the sky daily, ensuring life's cycle. He was associated with kingship and pharaohs, embodying resurrection and eternal life. His worship reached its peak during the New Kingdom, with temples and inscriptions celebrating his significance in ancient Egyptian spiritual and political life.
Admin
Egyptian cat goddess : Bastet ( God of ancient Egypt )
Bastet, an ancient Egyptian goddess, is primarily associated with home, fertility, joy, and motherhood, often depicted as a woman with the head of a domestic cat or as a lioness. Originally revered for her fierce protective nature, she later became a symbol of domesticity and nurturing. Commonly associated with music and dance, her worship centered in Bubastis, where vibrant festivals celebrated her qualities. Bastet embodies a dual nature, representing both gentleness and fierce protection, making her a vital figure in ancient Egyptian religion.
Admin
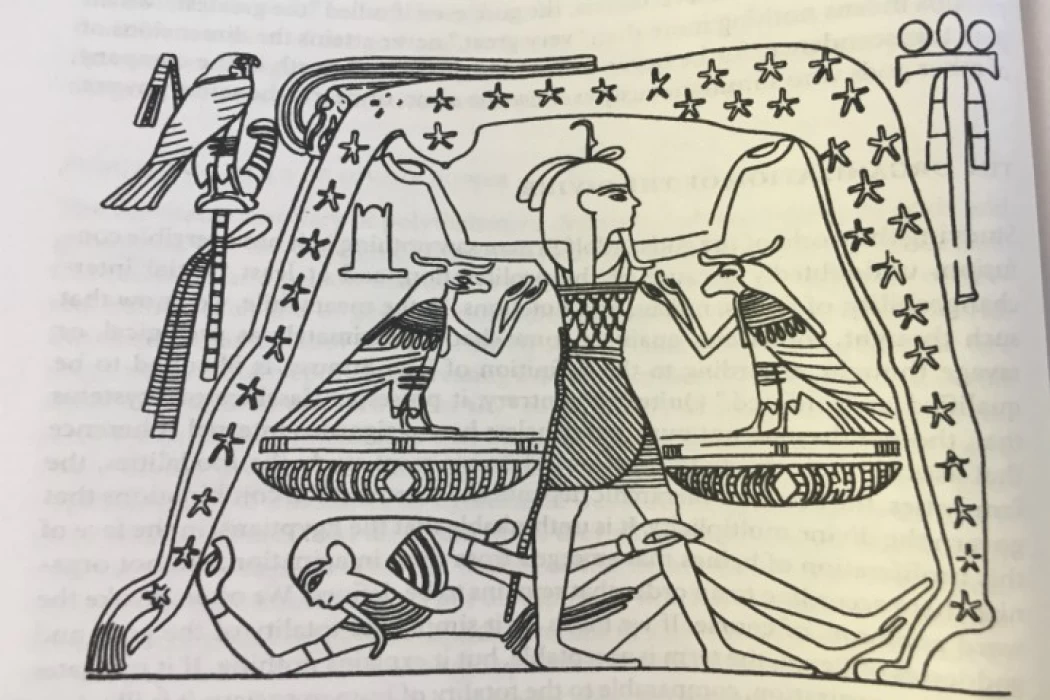
Ma'at- Explore Deities of Ancient Egypt
Maat, an ancient Egyptian goddess, symbolized truth, justice, and cosmic order. She was central to the Egyptian belief system, representing balance and harmony in the universe and society. Maat's principles guided pharaohs in governance and moral conduct, reflecting the concept of ma'at. In the afterlife, the deceased's hearts were weighed against her feather in a judgment ceremony, determining their fate based on their adherence to her values.
Admin
Neith: The Goddess Who Created the World
Net, or Neth, was an ancient Egyptian goddess associated with hunting, warfare, and protection. She was often depicted as a lioness, symbolizing strength and fierce motherhood. Worshiped in Sais, Net served as a guardian for pharaohs, providing divine support in battles. Net was also linked to fertility and childbirth, highlighting her nurturing side alongside her warrior attributes. Her dual nature emphasized the balance between creation and destruction.